Blockchain technology constantly evolves, bringing new possibilities and challenges to the decentralized world. One of the most promising projects in this field is the Stacks blockchain , which aims to enhance the functionality and potential of the Bitcoin network.
By introducing an innovative contract platform that leverages Bitcoin's security and trust, the Stacks blockchain offers a new way of creating and interacting with digital assets, smart contracts, and decentralized applications. In this article, we will explore the main features, use cases, benefits, and drawbacks of the Stacks blockchain.
How Does the Stacks Blockchain Work?
The Stacks blockchain is a new blockchain connected to the Bitcoin network. The Bitcoin network is the oldest and most secure blockchain in the world, and it uses a system called Proof of Work (PoW) to validate transactions and create new blocks. PoW means that the nodes (computers) that participate in the network have to solve complex mathematical problems to prove that they have done some work. This work requires a lot of computing power and energy, making the network very secure because it is tough for anyone to cheat or attack the network.
However, PoW also has some drawbacks. It is slow because solving the problems and reaching a consensus among the nodes takes time. It is also limited because it can only process a certain number of transactions per second. And it is not very flexible because it does not allow for smart contracts or other advanced features.
PoX. Image Credit: Stacks
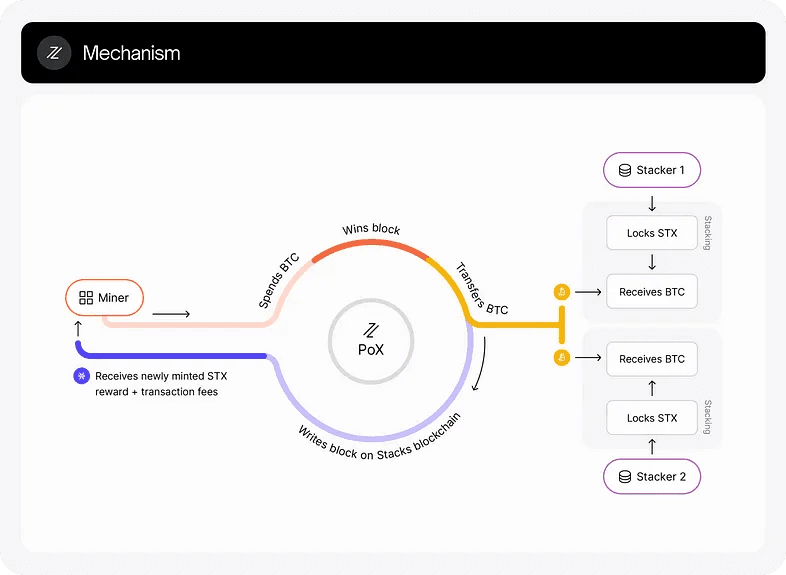
The Stacks blockchain wants to overcome these drawbacks using a different system called Proof of Transfer (PoX). PoX is an extension of another technique called Proof of Burn (PoB), similar to PoW. Still, instead of using computing power and energy, it uses an existing cryptocurrency (such as Bitcoin) to secure a new blockchain. PoB means that the nodes that participate in the network have to burn (destroy) some amount of the cryptocurrency to prove that they have done some work. This work does not require any special hardware or energy, and it makes the network secure because it is very costly for anyone to cheat or attack the network.
However, PoB also has some drawbacks. It is wasteful because it destroys valuable cryptocurrency that could be used for other purposes. It is also not very rewarding because it does not incentivize the nodes to participate in the network.
The Stacks blockchain solves these drawbacks by using PoX instead of PoB. PoX is similar to PoB, but instead of burning the cryptocurrency, it transfers it to other network participants. These participants are called stackers, and they are users who lock up some amount of the Stacks cryptocurrency (the native token of the Stacks blockchain) for a certain period. By doing so, they support the security and stability of the network, and they receive rewards in Bitcoin from the nodes that transfer it.
This way, PoX creates a win-win situation for the nodes and the stackers. The nodes can secure the Stacks blockchain without wasting Bitcoin or competing with the network for resources. The stackers can earn Bitcoin without doing work or risking their Stacks tokens. And both can benefit from the features and functionalities of the Stacks blockchain, such as smart contracts and decentralized applications.
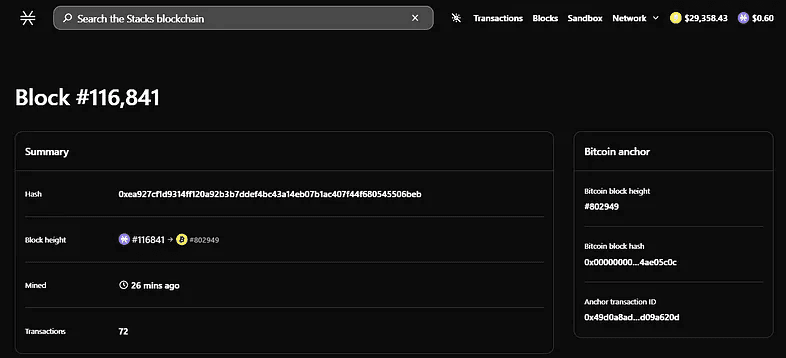
Stacks Explorer powered by Hiro. Each Block is mapped to the Bitcoin block.
How does Stacks enable smart contracts since the Bitcoin network uses Bitcoin Script, which is Turing Incomplete?
Stacks enables smart contracts by using a different programming language and execution environment than Bitcoin. Bitcoin uses a scripting language called Bitcoin Script, which is intentionally limited in its functionality and expressiveness. This makes Bitcoin Script secure and predictable but also prevents it from supporting complex logic and computation. Bitcoin Script is Turing incomplete, meaning it cannot perform arbitrary calculations or loops.
Stacks uses a programming language called Clarity , which is explicitly designed for smart contracts. Clarity is more expressive and powerful than Bitcoin Script, allowing developers to write complex logic and computation. Clarity is also Turing complete, meaning it can perform any calculation or loop that is theoretically possible. However, Clarity is also designed to be safe and predictable, avoiding some common pitfalls and vulnerabilities of other smart contract languages.
Clarity smart contracts run on the Stacks blockchain, a separate layer from the Bitcoin blockchain. The Stacks blockchain is connected to the Bitcoin blockchain by a novel consensus mechanism called Proof of Transfer (PoX). PoX allows the Stacks blockchain to inherit the security and finality of the Bitcoin blockchain while also enabling faster transactions and scalability. PoX also allows the Stacks blockchain to interact with the state of the Bitcoin blockchain, such as reading the balance or transactions of a Bitcoin address.
Therefore, Stacks enables smart contracts by using a different layer, language, and consensus mechanism than Bitcoin while still leveraging Bitcoin's security and state.
This means developers can build decentralized applications that benefit from Bitcoin's security and stability while adding new functionalities and features. In other words, the Stacks blockchain bridges the gap between the versatility of smart contracts and the reliability of the Bitcoin blockchain.
What Can You Do with the Stacks Blockchain?
The Stacks blockchain enables a variety of use cases that can transform how we interact with digital assets, smart contracts, and decentralized applications. Some of these use cases are:
- Decentralized Applications (DApps) on Bitcoin: The Stacks blockchain allows developers to create DApps that run on the Bitcoin network, taking advantage of its strong network effect and proven track record for security. This opens up new possibilities for innovation and experimentation in the decentralized space.
- Tokenization and Digital Assets: The Stacks blockchain enables the creation of native tokens representing any digital or physical asset. This can lead to new forms of asset ownership, such as fractional ownership of real estate, art, and more. It can also facilitate cross-border payments and remittances by streamlining the transfer of value.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): The Stacks blockchain supports the development of DeFi protocols that operate within the Bitcoin ecosystem. This can provide more inclusive and secure financial services without requiring users to switch to other blockchains or platforms.
- Privacy and Security: The Stacks network prioritizes user privacy and data ownership. It provides features that allow users to manage their data, ensuring they can use applications without compromising their personal information.
- Decentralized Identity (DID): The Stacks blockchain enables the creation of decentralized identity solutions, which give users control over their digital identity and reduce their dependence on centralized platforms.
What are the Benefits of the Stacks Blockchain?
The Stacks blockchain offers several advantages, making it an attractive option for developers and users. Some of these advantages are:
- Security: The Stacks blockchain inherits its robust network and attack resistance by building on Bitcoin's security model.
- Interoperability: The Stacks blockchain's layer-1 smart contracts can communicate with other blockchains, allowing for seamless integration and cross-chain interaction.
- Scalability: The Stacks blockchain's PoX consensus mechanism leverages Bitcoin's security while enabling faster transaction finality and increased scalability.
- Decentralization: The Stacks blockchain contributes to a more decentralized and diverse blockchain ecosystem by bringing smart contracts to Bitcoin.
- Ecosystem Growth: The Stacks blockchain fosters innovation and growth by providing developer-friendly tools and an active community.
What are the Challenges or Limitations of the Stacks Blockchain?
The Stacks blockchain has its challenges and limitations. Some of these are:
- Learning Curve: The Stacks blockchain's unique design may require developers and users to learn new concepts and skills before fully utilizing its potential.
- Adoption: The Stacks blockchain's success depends on its adoption by developers and users, which may take time and effort.
- Competition: The Stacks blockchain faces competition from other projects that offer similar or alternative solutions to the challenges of decentralization.
- Regulation: The Stacks blockchain may encounter regulatory hurdles or uncertainties that could affect its development or operation.